Digital Forensics and Memory Analysis for Malware Investigation
Conducted a detailed forensic investigation of five memory dumps (0zapftis.vmem, Coreflood.vmem, Memory.mem, Zeus.vmem, WindowsXPProfessional.vmem) from suspected malware-infected systems. Extracted critical forensic artifacts, identified malicious processes, and determined the malware name and family to understand its behavior and potential impact.
Steps
Step 1: Collected five memory dump files (0zapftis.vmem, Coreflood.vmem, Memory.mem, Zeus.vmem, WindowsXPProfessional.vmem) and verified integrity before starting analysis.
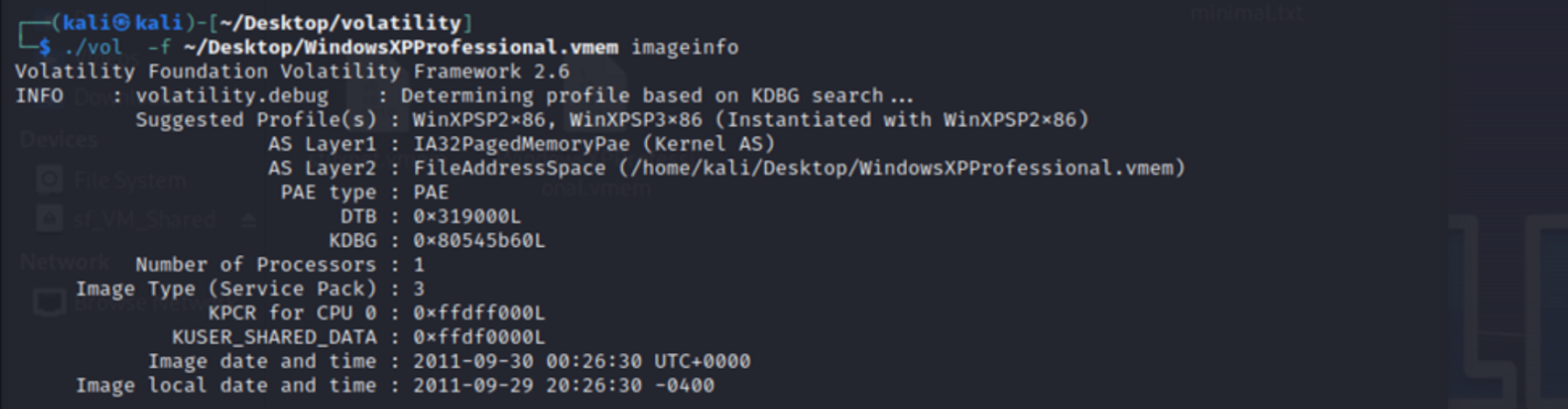
Step 2: Used Volatility's `imageinfo` plugin to determine the correct profile for each memory dump, ensuring accurate parsing and analysis.
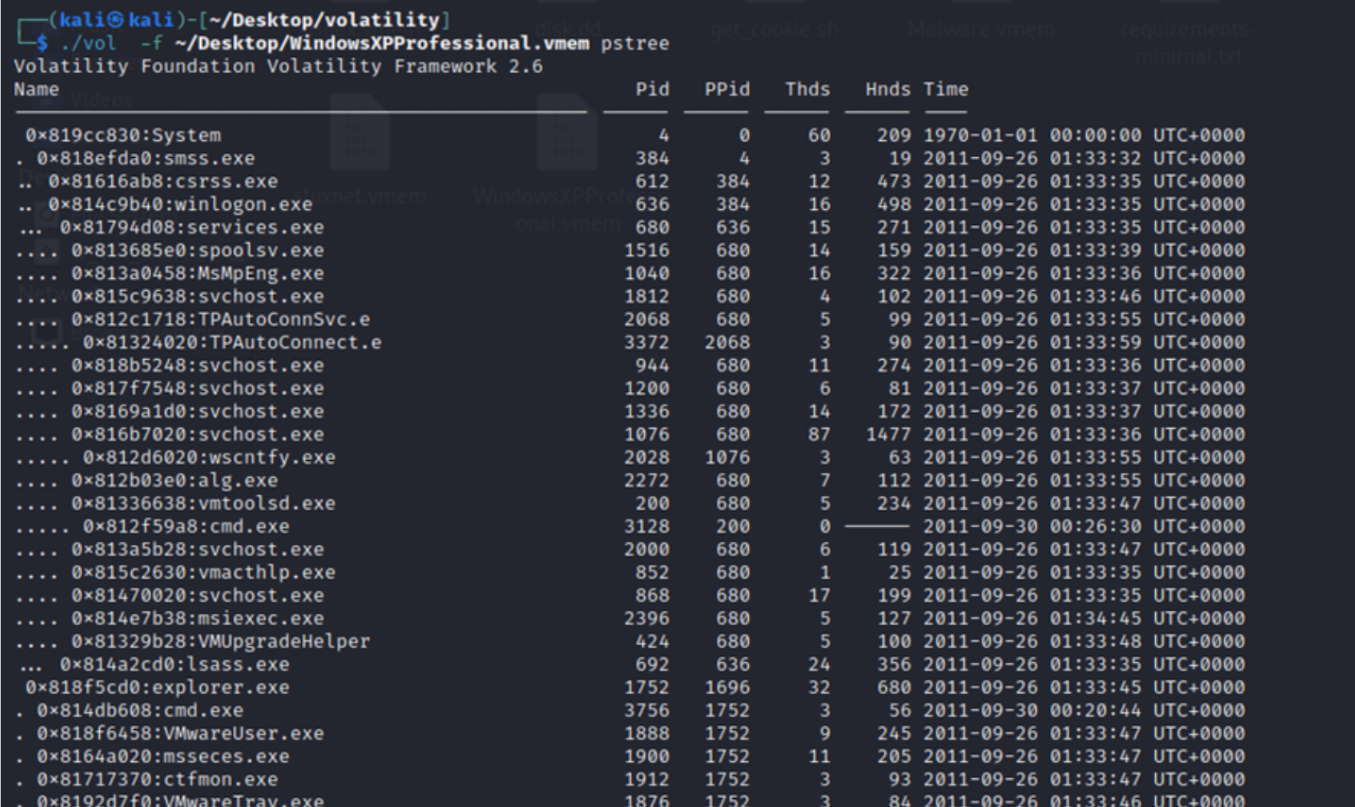
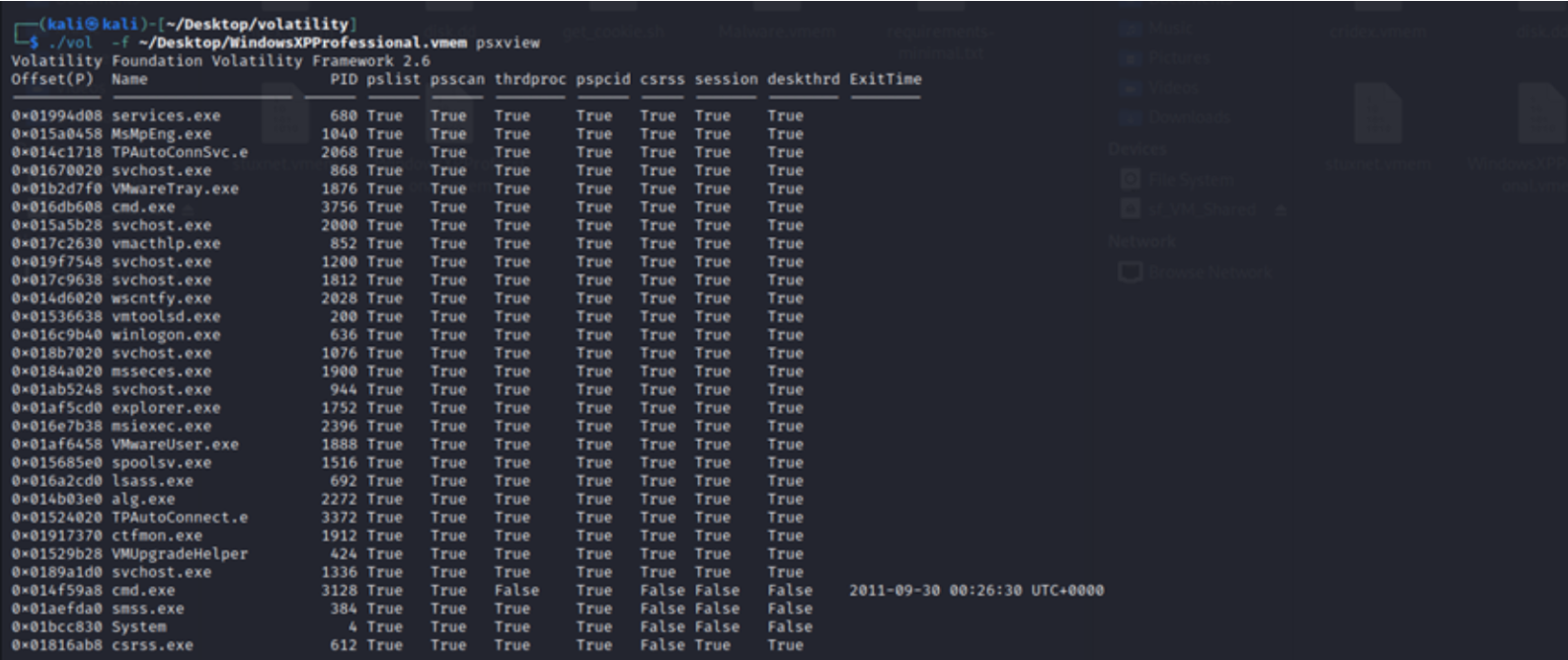
Step 3: Ran Volatility plugins such as `pslist`, `pstree`,`psxview` ,dlllist`, and `netscan` to extract active processes, loaded modules, and open network sockets for each memory image.
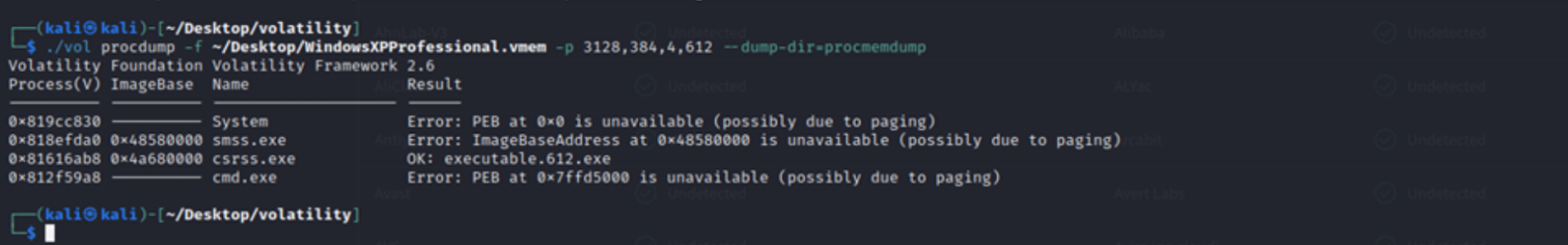
Step 4: Dumped suspicious processes using `procdump`, reviewed command history with `cmdscan`, and analyzed registry hives, kernel memory, and configuration files for indicators of compromise (IOCs).
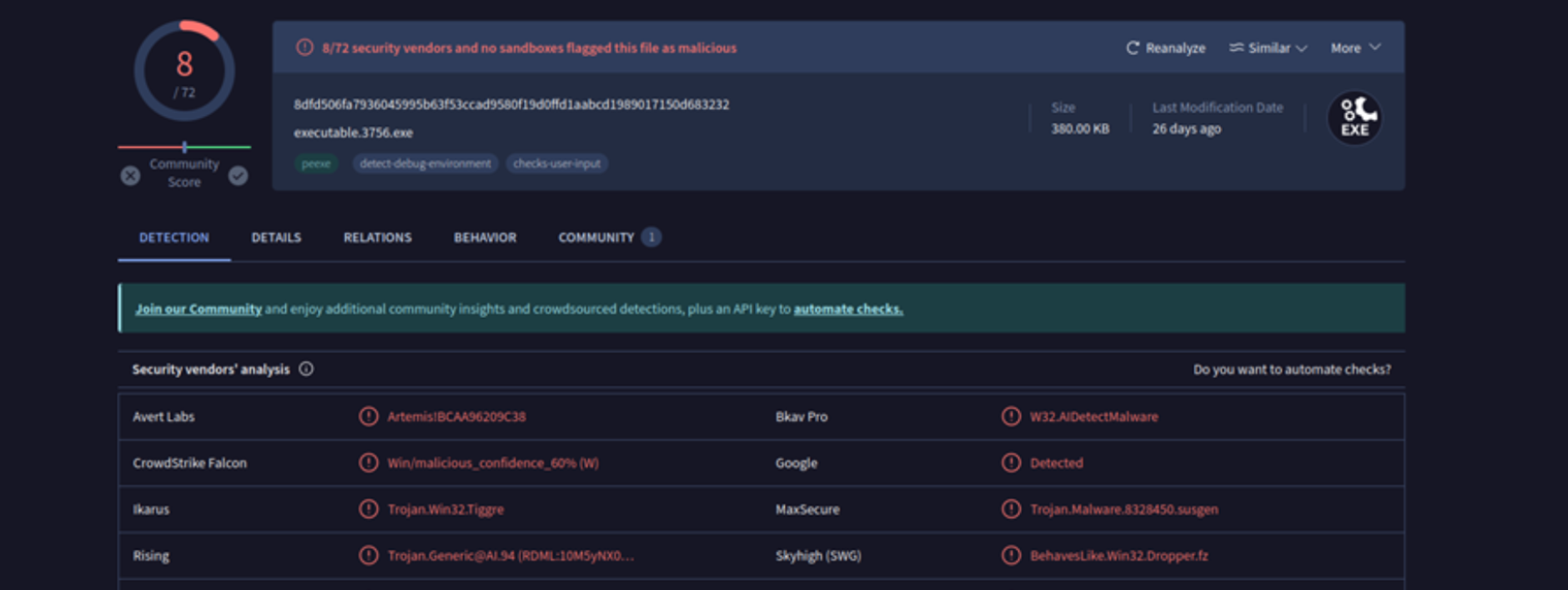
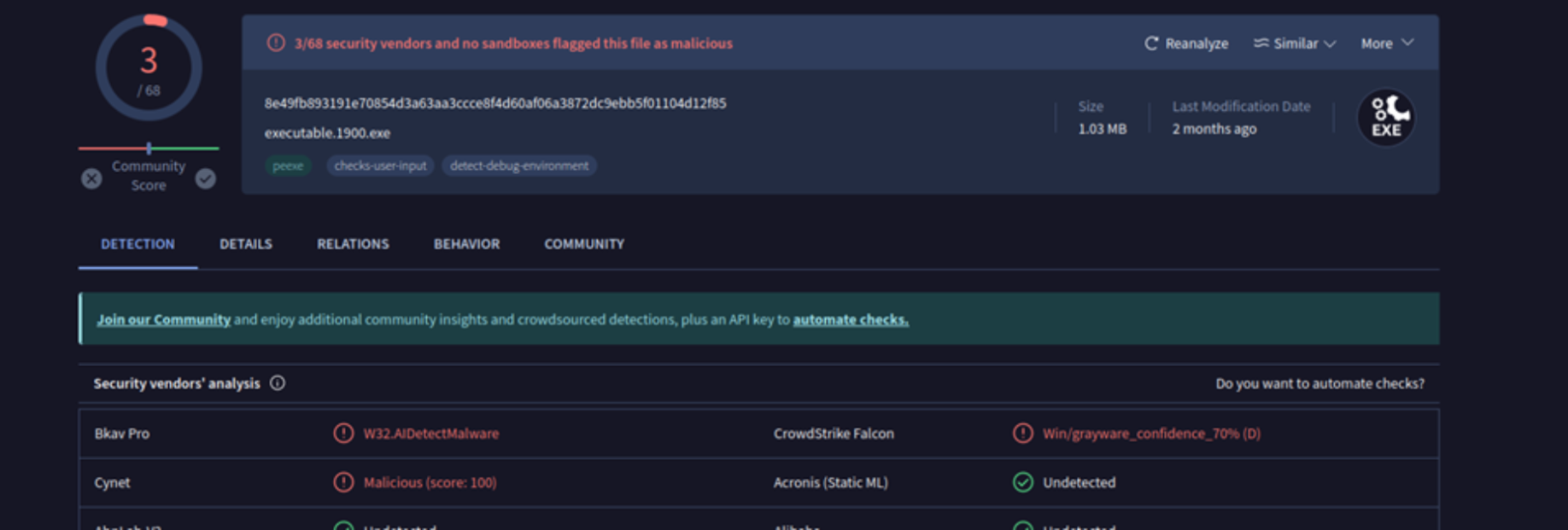
Step 5: Submitted dumped binaries and suspicious artifacts to VirusTotal and cross-referenced results with known malware families (e.g., Coreflood, Zeus).
Step 6: Identified persistence mechanisms, C2 communication patterns, and potential system impact. Compiled a final forensic report with recommendations for containment, eradication, and recovery.
Tools
Volatility Framework, VirusTotal, Memory Analysis Tools
Frameworks
Digital Forensics, Malware Analysis, Incident Response
Standards
NIST SP 800-61 (Computer Security Incident Handling Guide), ISO/IEC 27037 (Digital Evidence Collection)